Mapping in Ancient World: Foreigners Stated India as Rectangular, Puranas as Inverted Triangle
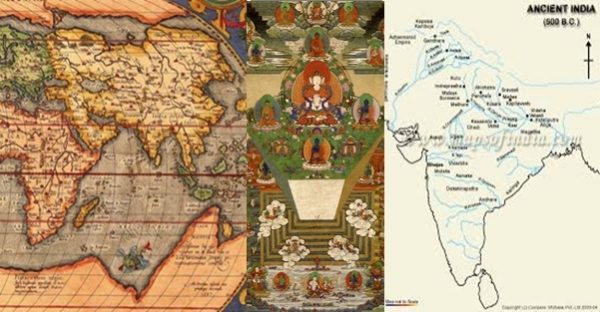
All Greek-Roman writers since Herodotus stated India as rectangular whereas all Purāṇas tell it as inverted triangle which gave the name Kumārikā Khaṇḍa as viewed from south ocean.
Mapping
Mapping needs measure of 3 quantity (Tri-praśna) at key points on globe – (a) Longitude, (b) Latitude, (c) Direction (marking north). These need observing Nakṣatra in space in Spherical polar coordinates.
Parilekha is a measure (Māpa), so it is Map. Uses Nakṣatra, so Nakshā. Measurement of latitude is considered easiest, but that needs accurate southern declination of sun or any reference star. Longitude needs accurate measurement of time hence its method was not known in Europe till 1480. Only after it was learnt from India via Turkey navy, Columbus could plan his America visit. Actually, an old map was stolen from Turkey from Admiral Piri Reis, which showed Americas and Antarctica. Provisions were kept only for visit to America about 2500 kms away, visit to India would have needed journey of 18000 kms. Maps of India by Europeans till 1780 showed India as rectangular. See link here.
All Greek-Roman writers since Herodotus stated India as rectangular whereas all Purāṇas tell it as inverted triangle which gave the name Kumārikā Khaṇḍa as viewed from south ocean. Inverted triangle is called Śakti-trikoṇa and Kumārī is root form of Śakti.
मत्स्य पुराण, अध्याय ११४-अयं तु नवमस्तेषं द्वीपः सागरसंवृतः। योजनानां सहस्रं तु द्वीपोऽयं दक्षिणोत्तरः।९।
आयतसु कुमारीतो गङायाः प्रवहावधिः।तिर्यगूर्ध्वं तु विस्तीर्णः सहस्राणि दशैव तु।१०।
Megasthenes: Indika (FRAGMENT I OR AN EPITOME OF MEGASTHENES. (Diod. II. 35-42.): India, which is in shape quadrilateral, has its eastern as well as its western side bounded by the great sea, but on the northern side it is divided by Mount Hemodos from that part of Skythia which is inhabited by those Skythians who are called the Sakai, while the fourth or western side is bounded by the river called the Indus, which is perhaps the largest of all rivers in the world after the Nile. The extent of the whole country from east to west is said to be 28,000 stadia, and from north to south 32,000.
Map References
Quadrant points-Marking 4 points separated by ¼ of circle-It is not clear whether 4 cardinal towns were built at distance of quadrant or after being built, they were found approximately at quadrant from each other.
(1) Brahmā system (29102 BC) in Purāṇas.
(2) Vaivasvata Manu system (13902 BC) in Sūrya-Siddhānta by Vivasvān (Sun).
Ref. East (+900) West (-900) Opposite (+1800, or-)
Amarāvatī Sukhā Sanyamanī Vibhāvarī
(Indra) (Varuṇa) (Yama) (Soma)
Ujjain (Lankā) Yamakoṭipattan, Romakapattana, Siddhapura
(Bhārata) (Ketumāla) (Bhadrāśva) (Uttara-Kuru).
विष्णु पुराण (२/८)-मानसोत्तरशैलस्य पूर्वतो वासवी पुरी।
दक्षिणे तु यमस्यान्या प्रतीच्यां वारुणस्य च। उत्तरेण च सोमस्य तासां नामानि मे शृणु॥८॥
वस्वौकसारा शक्रस्य याम्या संयमनी तथा। पुरी सुखा जलेशस्य सोमस्य च विभावरी।९।
शक्रादीनां पुरे तिष्ठन् स्पृशत्येष पुरत्रयम्। विकोणौ द्वौ विकोणस्थस्त्रीन् कोणान्द्वे पुरे तथा।॥१६॥
उदितो वर्द्धमानाभिरामध्याह्नात्तपन् रविः। ततः परं ह्रसन्तीभिर्गोभिरस्तं नियच्छति॥१७॥
(सूर्य सिद्धान्त १२/३८-४२)-भूवृत्तपादे पूर्वस्यां यमकोटीति विश्रुता। भद्राश्ववर्षे नगरी स्वर्णप्राकारतोरणा॥३८॥
याम्यायां भारते वर्षे लङ्का तद्वन् महापुरी। पश्चिमे केतुमालाख्ये रोमकाख्या प्रकीर्तिता॥३९॥
उदक् सिद्धपुरी नाम कुरुवर्षे प्रकीर्तिता (४०) भूवृत्तपादविवरास्ताश्चान्योन्यं प्रतिष्ठिता (४१)
तासामुपरिगो याति विषुवस्थो दिवाकरः। न तासु विषुवच्छाया नाक्षस्योन्नतिरिष्यते ॥४२॥
These quadrants are 4 petals of Earth- lotus, Bhārata covers
(विष्णु पुराण २/२)-भद्राश्वं पूर्वतो मेरोः केतुमालं च पश्चिमे। वर्षे द्वे तु मुनिश्रेष्ठ तयोर्मध्यमिलावृतः।२४।
भारताः केतुमालाश्च भद्राश्वाः कुरवस्तथा। पत्राणि लोकपद्मस्य मर्यादाशैलबाह्यतः।४०।
Rotation axis is Meru, north pole = Sumeru, South pole = Kumeru.
(आर्यभटीय ४/११-१४)-मेरुर्योजनमात्रः प्रभाकरो हिमवता परिक्षिप्तः। नन्दनवनस्य मध्ये रत्नमयः सर्वतो वृत्तः॥११॥
स्वर्मेरु स्थलमध्ये नरको बडवामुखं च जलमध्ये। अमरमरा मन्यन्ते परस्परमधः स्थितान् नियतान् ॥१२॥
Local references in each continent, countries-local Merus,
North Hemisphere-4 quadrants in 4 colours = 4 colours of Sumeru faces.
Similarly, 4 quadrants in south= Total 8 petals of earth,
Bhārata petal in north-divided into 3 or 7 lokas like lokas in space.
ब्रह्माण्ड पुराण उपसंहार पाद, अध्याय २ (३/४/२)-
लोकाख्यानि तु यानि स्युर्येषां तिष्ठन्ति मानवाः॥८॥ भूरादयस्तु सत्यान्ताः सप्तलोकाः कृतास्त्विह॥९॥
पृथिवीचान्तरिक्षं च दिव्यं यच्च महत् स्मृतम्। स्थानान्येतानि चत्वारि स्मृतान्यावर्णकानि च॥११॥
जनस्तपश्च सत्यं च स्थान्यान्येतानि त्रीणि तु। एकान्तिकानि तानि स्युस्तिष्ठंतीहाप्रसंयमात्॥१३॥
भूर्लोकः प्रथमस्तेषां द्वितीयस्तु भुवः स्मृतः।१४॥
स्वस्तृतीयस्तु विज्ञेयश्चतुर्थो वै महः स्मृतः जनस्तु पञ्चमो लोकस्तपः षष्ठो विभाव्यते॥१५॥
सत्यस्तु सप्तमो लोको निरालोकस्ततः परम्।१६। महेति व्याहृतेनैव महर्लोकस्ततोऽभवत्॥२१॥
यामादयो गणाः सर्वे महर्लोक निवासिनः।५१॥
(वायु पुराण, अध्याय १०१)-महेति व्याहृतेनैवं महर्लोकस्ततोऽभवत्।
विनिवृत्ताधिकाराणां देवानां तत्र वै क्षयः॥२३॥ यामादयो गणाः सर्वे महर्लोकनिवासिनः॥५२॥
Trilokī of Indra
Bhārata, Chīna, Ṛṣīka (Russia) with Śivira (Siberia), Nivāta-kavacha (very cold region needing wind-cheaters). Each are divided into 3 parts, middle parts come in parts of both sides, so there are 7 lokas in Deva-part (Bhārata petal of north hemisphere) –
(1) Bhū-Equator to Vindhya
(2) Bhuvah-Vindhya to Himālaya-called Madhyadeśa (Madhes in Nepal, Medes in Bible, another Medes north-west of Iran)-King of Ayodhyā has been called king of middle loka-अन्वग्ययौ मध्यम लोकपालः (रघुवंश २/१६)
(3) Svah (Svarga)-Himālaya region in Bhārata is divided into 3 Viṣṭapa or Viṭapa (Tree, catchment area of river)-(a) Viṣṇu-viṭapa in west is drained by Sindhu river system-place of Vaiṣṇo Devī. Lakṣmī is daughter of Sindhu & wife of Viṣṇu. This region Kashmir is heaven on earth. (b) Śiva-viṭapa is region around Kailāsa-Mānasarovara drained by Gangā system-from hairs of Śiva. (c) Brahma-viṭapa is drained by Brahmaputra and land east of that is Brahma-desha (now Myammar = Mahā + Amara, or head among Devas). 3 Vitapas combined are Triviṣṭapa = svarga (Tibet).
(4) Mahar-China is next part called Mahar as its people were called Mahā (Han) by Brahmā.
(5) Jana-Mangolia is Janah loka-In space Janah loka is galaxy which is final destination of soul-ध्रुवादूर्ध्वं महर्लोको यत्र ते कल्पवासिनः । एकयोजनकोटिस्तु यत्र ते कल्पवासिनः॥१२॥
द्वे कोटी तु जनो लोको यत्र ते ब्रह्मणः सुताः। सनन्दनाद्याः प्रथिता मैत्रेयामलचेतसः॥१३॥(विष्णु पुराण २/७)
In Arabic, mukul = preta = pra +itah (soul which has departed from body). Parallel to place of Mukul on earth is Mukul = Mangolia.
(6) Tapah loka-Ṛṣīka deśa where Arjun had stopped his northward conquest. Śivira (Siberia-temporary tents in snow), Nivāta-kavacha (very cold place, wind cheaters used).Tapas has become Steppes.
(7) Satya loka-Polar circle-north boundary of Jambū-dvīpa is bow shaped like north boundary of Bhārata, which is Himālaya-
भारतं प्रथमं वर्षं ततः किम्पुरुषं स्मृतम्।.. उत्तराः कुरवश्चैव यथा वै भारतं तथा॥(विष्णु पुराण २/२/१३-१४)
In space, average energy or temperature oh higher (bigger) lokas is successively lower. In Indra region also, lokas to north are colder.
Other 7 petals (3 in north, 4 in south) are 7 Tala (or Pātāla), named differently in Purāṇas- Viṣṇu-Atala, Vitala, Nitala, Gabhastimat, Mahātala, Sutala, Pātāla. Brahmāṇḍa-Tatvala, Sutala, Talātala, Atala, Tala, Rasātala, Pātāla. Bhāgavata-Atala, Vitala, Sutala, Talātala, Mahātala, Rasātala, Pātāla.
विष्णु पुराण (२/५)-दशसाहस्रमेकैकं पातालं मुनिसत्तम।
अतलं वितलं चैव नितलं च गभस्तिमत्। महाख्यं सुतलं चाग्र्यं पातालं चापि सप्तमम्॥२॥
Plane projection of earth map will have infinite scale in polar region. That is not a problem for north hemisphere where north pole is in water. But south pole is land mass, whose scale will be infinite, so it is called Ananta and its map has to be made separately.
विष्णु पुराण (२/५)-पातालानामधश्चास्ते विष्णोर्या तामसी तनुः। शेषाख्या यद्गुणान्वक्तुं न शक्ता दैत्यदानवाः॥१३॥
योऽनन्तः पठ्यते सिद्धैर्देवो देवर्षि पूजितः। स सहस्रशिरा व्यक्तस्वस्तिकामलभूषणः॥१४॥
7 Dvīpas & oceans are actual land masses & natural divisions. Dvīpas are divided into Varṣa which are zones of Varṣā (rains).
4.
Meru of world map in 4 colours
Each quadrant of world was mapped in different colours. 4 colour system still continues. There is a 4-colour theorem in Topology. Each quadrant has a Meru like Jambū dvīpa has in Ilāvṛtta varṣa-
मत्स्य पुराण ११३-चातुर्वर्ण्यस्तु सौवर्णो मेरुश्चोल्बमयः स्मृतः।१२।
नाभीबन्धनसम्भूतो ब्रह्मणोऽव्यक्तजन्मनः।पूर्वतः श्वेतवर्णस्तु ब्राह्मण्यं तस्य तेन वै।१४।
पीतश्च दक्षिणेनासौ तेन वैश्यत्वमिष्यते।भृङ्गिपत्रनिभश्चैव पश्चिमेन समन्वितः।
पार्श्वमुत्तरतस्तस्य रक्तवर्णं स्वभावतः। तेनास्य क्षत्रभावः स्यादिति वर्णाः प्रकीर्तिताः।१६।
मध्ये त्विलावृतं नाम महामेरोः समन्ततः।१९।
मध्ये तस्य महामेरुर्विधूम इव पावकः। वेद्यर्थं दक्षिणं मेरोरुत्तरार्धं तथोत्तरम्।२०।
Meru for each continent & local maps
Jaina Harivamśa purāṇa specifically indicates separate Merus for each continent-जैन हरिवंश पुराण (पञ्चम सर्ग)-
पूर्वापरौ महामेरोर्द्वौ मेरू भवतोऽस्य च। इष्वाकारौ विभक्तारौ पर्वतौ दक्षिणोत्तरौ॥४९४॥
अशीतिश्च सहस्राणि चत्वारि च समुच्छ्रयः। चतुर्णामपि मेरूणां परयोर्द्वीपयोर्भवेत्॥५१३॥ (धातकी खण्ड, पुष्कर द्वीप)
पुष्करिण्यः शिलाकूट प्रासादाश्चैत्य चूलिकाः। समानाः पञ्चमेरूपां व्यासादवगाहनोच्छ्रयैः॥५३०॥
तत्त्वार्थ वृत्ति, तृतीय अध्याय-तन्मध्ये मेरुनाभिर्वृत्तो योजनशतसहस्रविष्कम्भो जम्बूद्वीपः॥९॥
Even local map references of each major country have been called Meru-
1. Meru, Tanzania, a village in northern Tanzania (Arumeru District). It is inhabited by the Meru people of Tanzania, known as the “Wameru” in Bantu. Mount Meru is a volcano near Arusha in northern Tanzania 3°14′ S, 36°45′ E
2. Nearby Mount Kilimanjaro at 3°4′33″S, 37°21′12″E is in Kenya. Mount Kenya is at 0°9′00″S 37°18′00″E with nearby Meru Town at 0°03′N 37°39′E. There are Meru central and north districts, Maara district. Its people are called Ameru, their language is Kimiiru. The forest region is Meru National Park.
3. Meru, Hazaribagh, a small town in Jharkhand, India, 24°1′46″ N, 85°27′26″ E. This is almost at old Karka rekhā and about 100 east of Ujjain, thus a local reference.
4. Meru, Malaysia, a town in Klang, located in Selangor, 308’ N, 101027’ E
5. Meru, Western Australia, a locality near Geraldton, 28°48′11″S 114°41′10″E
6. Méru, a commune of the Oise département in France 490 14’N, 20 8’ E- about 73045’ west of Ujjain or 12 time zone west. Place of Time zones are places of Śiva called Mahākāla at Ujjain at central longitude. Similarly, town near Greenwich longitude here is called Lourdes (Rudreśa) at 4306’ N and 003’ E.
7. Meru Peak, a mountain in the Indian Himalayas 30°52′5″N, 79°1′56″E
8. Phra Sumeru Temple, Bangkok, Thailand,13°45’N 100°35’E
9. Sumeru mountain, Java, 806’S, 120035’E
10. Mount Sumeru of China at 36°01′N 106°15′E is of red sandstone like colours of Meru in Purāṇas. It is full of minerals.
Minor References
Like present time-zones at interval of 30 minutes, ancient time zones of world were at intervals of 60 or 24 minutes (=1 daṇḍa). These were places of sun, Lankā, of places of time (Kāla). Central place of time was Mahā-kāla (Great time) in Ujjain, whose central point appears to be point on prime meridian. Kālahastī in Andhra Pradesh is 60 east of Ujjain. Koṇārka at east coast in Orissa is 120 east of Ujjain. Kālapriya (Kālapī in Uttar pradesh) and Mūlasthāna (Multan in west Punjab) are at 00 and 60 west. Lolārka in Vārāṇasī and Puṇyārka (Punarakh near Patna,Bihar) are also 60 and 90 east of Ujjain. Thaneswar is at 00 long. Puṣkara (present Bukhara in Ujbekistan) was 120 west of Ujjain as per Viṣṇu Purāṇa (2/8/26).
Kyoto (old capital of Japan, 600 east), Pyramid of Ezypt (450 west), Ancient capital of Inkā (Ina = sun in Sūrya-Siddhānta) in Peru is 1500 west-all were places of kings of sunrace. Stonehenge in England was 780 west (13 time zones). It was place of observatory and its region is called Lancashire, Lancaster. Lourdes Rudreśa) in France onits east border is old holy place and is 720 west (12 time zones). Hellespont (helios = sun) is narrow sea between old south Greece and Turkey, now called Dardanelles. This and places in Turkey-Izmir (Meru) and Canakkate (Koṇārka = place of arka=sun) are 420 west.
Survey Centres
(a) Guntur-Guṇṭha = small area, measure rods linked together.
Ur (Uru) = town, Centre of Survey is Guntur. Gunter chain = 100 links = 22 m
(b) Ranchi-Zero ref point (RD)-town measures from this place.
Indra (Achyuta-chyuta) ref-Chutiya in Ranchi,
Dhruva (fixed pole) measuring rod. Dhurva region, Dhura = 99” rod, its squire land
(c) Karachi-RD point for ocean distances (Ka = water).
(d) Other RD points-Kumbhakoṇam-Kaveri Delta is Kumbha (water pot), Its mouth is Kumbhakoṇam (koṇa = angle).
Konkaṇa or Koṇagaḍha (like Koṇārka)-Reference of map or time zone.
Kanyākumārī-End point of Kumārikā Khaṇḍa (Bhārata as inverted triangle). Kumārikā in ocean in south hemisphere (now called Indian ocean in same sense).
Road-Sea Routes, Maps
Fahien had expressed surprise that the Indian ship from Tamralipti to China carried 1500 persons and did not follow coast line. It could navigate in deep sea and new locations of turning points like Andaman and Singapore.
Town Designs
(a) Uru, (b) Pura, (c) Meru, (d) Vajra, (3) Śrī (Trikoṇa -Thiru) – All these provide for drainage of water.
Uru is like Urvī (earth sphere) whose central point is topmost (Bangaluru, Mangalore, Nellor, Chittur of AP, Chittor of Rajsthan).
Pura is rectangular matrix of roads. Drainage from one side of rectangle to opposite side.
Meru has shape like 4 faced pyramid of Meru mountain, but very gentle slopes (Ajayameru = Ajmer, Jaisalmer).
Vajra is on both sides of a river. Triangles on both sides join to form a rectangle with river as diagonal. Old Vajra town is Basra of Iraq.
Śrī is in shape of Śrī-yantra = nine concentric circles with central point at top sloping down outwards-Srinagar in Kashmir, Garhwal, Srividyanagara (Vijayanagara), Tiru-anantapuram. Tiruchirapalli.
Map of country-names on map shape-
Kumārikā Khaṇḍa (Inverted triangle, Śakti-trikoṇa)
Lankā-long in north south on Ujjain longitude-Lanka = chilly in Bengal, Odisha.
वाल्मीकिरामायण,उत्तरकाण्ड–
त्रिंशद्योजनविस्तीर्णाशतयोजनमायता। (५/२५) मयालङ्केतिनगरीशक्राज्ञप्तेननिर्मिता॥ (५/२६)
All astronomy texts tell it on same longitude as of Ujjain. Present Srilanka was Simhal, politically part of Lanka in time of Ravana.
Kerala= Chera (at root of country)-name of a kingdom, vegetable of this shape = Karela.
Jambū-dvīpa-Relief map of Manipur region = head of elephant
Śuṇḍā (elephant trunk)-shape of Indonesia-Greater & smaller Shunda groups
Himalaya in crescent shape, so Bhārata is Indu = Inde (India)-Huensang.
North boundary of Jambū-dvīpa also like that.
Krauñcha (Heron) dvīpa-Shape of north America. This has been called west of Meru and in north (Mahābhārata 12/14/21-25, 16/25). Bṛhat Samhitā and Rāmāyaṇa locate it in north. Thus it is North America which has Rockies mountain in same shape of a flying bird (krauñcha).
Featured image courtesy: Wikipedia, Maps of India, and Pinterest.






